Nourishing the Heart: A Science-Based Overview on Why Nutrition Is Foundational In Heart Disease Care
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States, yet it’s also one of the most preventable and manageable chronic conditions. A heart-healthy diet is one of the most powerful tools for preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD). Decades of research show that what we eat profoundly influences heart health, risk factors, and long-term outcomes.
How Nutrition Shapes Heart Health
Nourishing dietary patterns—rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, fish, and heart healthy oils—consistently lower the risk of heart disease, stroke, and related conditions. These diets, such as the Mediterranean and DASH diets, reduce inflammatory markers, improve cholesterol profiles, lower blood pressure, and support healthful body weight management [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]. In contrast, diets high in ultra-processed foods, red and processed meats, added sugars, saturated and trans fats, and excessive sodium increase cardiovascular disease risk [1] [3] [4] [5].
Key Dietary Components and Their Effects
Fruits & Vegetables: A high intake is linked to lower rates of coronary artery disease (CAD) and stroke [1] [3] [5].
Whole Grains & Fiber: Improve cholesterol levels, reduces blood pressure, and lower CVD risk [1] [3] [5].
Nuts, Seeds, Legumes: Provide unsaturated fats and plant protein, supporting heart health [3] [4] [5].
Fish & Omega-3’s: Associated with reduced risk of heart disease and improved vascular function [3] [4] [5].
Oily Fats: Replacing saturated and trans fats with unsaturated fats (from plants, nuts, seeds, and fish) lowers cholesterol and CVD risk [1] [3] [4] [5].
Limiting Sodium & Added Sugars: Reduces blood pressure and metabolic risk [1] [3] [4] [5].
Beyond Individual Nutrients: The Power of Dietary Patterns
Research consistently emphasizes that the overall dietary pattern (what, how, and when we eat day after day) matters more than any single nutrient on improving and supporting our heart health. The synergy of multiple foods and nutrients in a balanced dietary pattern provides greater protection than isolated supplements or single food changes [1] [2] [4] [5] [6] [7].
Nutrition and Heart Failure
Good nutrition is crucial for those with heart failure. Malnutrition significantly increases overall mortality risk, while appropriate dietary interventions can improve clinical outcomes and higher quality of life [8] [9] [10] [11].
Dietary Patterns and Heart Health Outcomes
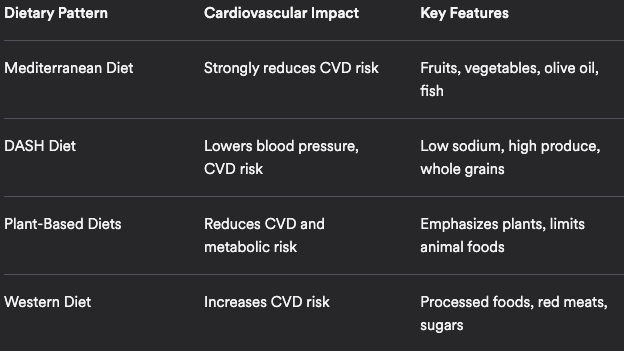
Figure 1. Comparison of dietary patterns and their cardiovascular effects. [1] [2] [4] [5] [13] [19]
Fortifying your emotional and mental health
A cardiovascular disease diagnosis not exist in a vacuum. Anxiety, depression, agitation, and stress often accompany cardiac diagnoses. Nutrition can play a vital role in supporting your heart and psychological health just the same! Balanced meals and snacks can aid in stabilizing mood, supporting brain health, and rebalancing energy levels that often come with blood sugar swings or nutritional deficiencies. Supporting your gut microbiota with adequate fiber and fermented food intake can positively support a healthier gut-brain axis connection affecting brain health, cognitive functioning, mood, and stress response. Sometimes food can be the best therapy [13] [14] [15]!
Overcoming Barriers to Heart-Healthy Eating
Challenges such as food insecurity, food deserts, targeted marketing of highly-processed foods and beverages, and socioeconomic disparities can impede access to a nutritious diets. Addressing these barriers public policy, federal funding support, and political advocacy is essential for improving heart health and decreasing cardiovascular disease risk at the population level [1] [6] [12].
Conclusion
A balanced, nutrient-rich diet is foundational for heart health and cardiovascular disease risk reduction. Emphasizing whole foods, unsaturated fats, and plant-focused meals/snacks—while limiting processed foods, saturated fats, excessive sodium, and added sugars—can dramatically reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall well-being.
At Wholehearted Nutrition and Wellness PLLC, we strongly believe that food is more than just fuel. It’s medicine, connection, enjoyment, and empowerment. We recognize why nutrition deserves center stage in cardiovascular disease management. If you’re interested in starting a heart healthy dietary pattern or learning how to manage your heart disease through nutrition, book an appointment with us today and begin your journey to better heart health.
References
1. Lichtenstein, A., Appel, L., Vadiveloo, M., Hu, F., Kris-Etherton, P., Rebholz, C., Sacks, F., Thorndike, A., Van Horn, L., & Wylie-Rosett, J. 2021 Dietary Guidance to Improve Cardiovascular Health: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021; 144. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001031
2. Casas, R., Castro-Barquero, S., Estruch, R., & Sacanella, E. Nutrition and Cardiovascular Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123988
3. Micha, R., Shulkin, M., Peñalvo, J., Khatibzadeh, S., Singh, G., Rao, M., Fahimi, S., Powles, J., & Mozaffarian, D. Etiologic effects and optimal intakes of foods and nutrients for risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses from the Nutrition and Chronic Diseases Expert Group (NutriCoDE). PLoS ONE. 2017; 12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175149
4. Mozaffarian, D. Dietary and Policy Priorities for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Obesity: A Comprehensive Review. Circulation. 2016; 133. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018585
5. Eilat-Adar, S., Sinai, T., Yosefy, C., & Henkin, Y. Nutritional Recommendations for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention. Nutrients. 2013; 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5093646
6. Diab, A., Dastmalchi, L., Gulati, M., & Michos, E. A Heart-Healthy Diet for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: Where Are We Now?. Vascular Health and Risk Management. 2023; 19. https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S379874
7. Bowen, K., Sullivan, V., Kris-Etherton, P., & Petersen, K. Nutrition and Cardiovascular Disease—an Update. Current Atherosclerosis Reports. 2018; 20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-018-0704-3
8. Yoshihisa, A., Kanno, Y., Watanabe, S., Yokokawa, T., Abe, S., Miyata, M., Sato, T., Suzuki, S., Oikawa, M., Kobayashi, A., Yamaki, T., Kunii, H., Nakazato, K., Suzuki, H., Ishida, T., & Takeishi, Y. Impact of nutritional indices on mortality in patients with heart failure. Open Heart. 2018; 5. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2017-000730
9. Wawrzeńczyk, A., Anaszewicz, M., Wawrzenczyk, A., & Budzyński, J. Clinical significance of nutritional status in patients with chronic heart failure—a systematic review. Heart Failure Reviews. 2019 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09793-2
10. Carime, N., Cottenet, J., Clerfond, G., Eschalier, R., Quilliot, D., Eicher, J., Joly, B., & Quantin, C. Impact of nutritional status on heart failure mortality: a retrospective cohort study. Nutrition Journal. 2022; 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-021-00753-x
11. Bianchi, V. Nutrition in chronic heart failure patients: a systematic review. Heart Failure Reviews. 2019; 25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09891-1
12. Mensah, G., Brown, A., & Pratt, C. Nutrition Disparities and Cardiovascular Health. Current Atherosclerosis Reports. 2020; 22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-0833-3
13. Suárez-López, L., Bru-Luna, L., & Martí-Vilar, M. Influence of Nutrition on Mental Health: Scoping Review. Healthcare. 2023; 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11152183.
14. Sarris, J., Sarris, J., Logan, A., Akbaraly, T., Akbaraly, T., Amminger, G., Balanzá-Martínez, V., Freeman, M., Hibbeln, J., Matsuoka, Y., Mischoulon, D., Mizoue, T., Nanri, A., Nishi, D., Ramsey, D., Rucklidge, J., Sánchez-Villegas, A., Scholey, A., Su, K., & Jacka, F. Nutritional medicine as mainstream in psychiatry. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2015; 23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(14)00051-0.
15. Loughman, A., Staudacher, H., Rocks, T., Ruusunen, A., Marx, W., Neil, A., & Jacka, F. Diet and Mental Health.. Modern trends in psychiatry. 2021; 32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000510422.